Impacts of Generative AI on Academic Integrity, Student Futures, and Industry Adoption in the UK
Table of Contents
1. Executive Summary
This report examines the multifaceted impacts of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) on academic integrity, student futures, and industry adoption, with a particular focus on the United Kingdom. As GenAI technologies rapidly evolve and permeate various sectors, they present both significant opportunities and challenges for education and industry. The report explores how UK universities are addressing GenAI integration, the potential risks to students’ future career prospects if not adequately educated about GenAI use, and the adoption and implementation of GenAI across various industries in the UK.
Key findings include:
- UK universities are proactively developing policies and initiatives to integrate GenAI into education while maintaining academic integrity.
- Students who lack education in GenAI face significant risks to their future career prospects, including reduced competitiveness in the job market and potential job displacement.
- The UK is emerging as a leader in GenAI adoption across industries, with significant investments and initiatives driving innovation and economic growth.
- Government policies and strategic frameworks are shaping the landscape of GenAI development and implementation in both education and industry.
This report aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state and future projections of GenAI’s impact on education and industry in the UK, offering insights for policymakers, educators, students, and industry leaders.
2. Introduction
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) has emerged as a transformative force in higher education and industry, reshaping teaching, learning, assessment practices, and business operations. As these technologies continue to evolve rapidly, they present both significant opportunities and challenges for academic institutions, students, and businesses.
This report investigates the implications of GenAI on academic integrity in higher education, explores the potential risks to students’ future career prospects if not adequately educated about GenAI use, and examines the adoption and implementation of GenAI across various industries, with a particular focus on the United Kingdom.
The objectives of this report are to:
- Examine how UK universities are addressing GenAI education and integration.
- Investigate the potential risks to students’ future career prospects if not educated about GenAI use.
- Research the adoption and implementation of GenAI in various industries, focusing on UK businesses where possible.
- Explore UK-specific policies, initiatives, and studies related to GenAI in education and industry.
By addressing these objectives, this report aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state and future projections of GenAI’s impact on education and industry in the UK, offering valuable insights for policymakers, educators, students, and industry leaders.
3. Generative AI in UK Higher Education
3.1 Policies and Guiding Principles
UK universities, particularly those in the Russell Group, have been proactive in addressing the challenges and opportunities posed by GenAI. The Russell Group universities, comprising 24 of the UK’s leading research institutions, have collectively issued five guiding principles to ensure ethical and effective use of GenAI tools. These principles emphasize:
- Supporting both students and staff to become AI-literate [1] [2].
- Training staff to assist students in using GenAI tools appropriately [3] [4].
- Adapting teaching and assessment methods to incorporate the ethical use of GenAI while maintaining academic integrity [5] [6].
- Ensuring equal access to GenAI tools for all students [6].
- Collaborating across institutions to share best practices as the technology evolves [7] [8].
Additionally, all Russell Group universities have updated their academic conduct policies to reflect the emergence of GenAI, providing clear guidelines on its appropriate use and addressing concerns such as plagiarism, bias, and inaccuracies [9] [10].
3.2 Institutional Initiatives and Frameworks
Several UK universities have launched specific initiatives and frameworks to integrate GenAI into their educational practices:
-
University of Birmingham:
- The university has introduced the “Birmingham Standards in Generative AI,” which outline principles for the ethical use of GenAI in teaching, learning, and assessment [11].
- Academic staff are encouraged to incorporate GenAI tools into course design and teaching activities while being mindful of their limitations and ethical implications [12] [13].
- The university emphasizes the need for regular reviews of teaching and assessment practices to adapt to the evolving capabilities of GenAI [14].
-
University of Oxford:
- Oxford has developed guidance for students on the ethical use of GenAI tools, emphasizing the importance of critical thinking, academic integrity, and proper attribution [15] [16].
- Students are encouraged to use GenAI tools for tasks such as summarizing key texts, generating practice questions, and analyzing data sets [17] [18] [19].
- The university also highlights the need for students to cross-check AI-generated outputs against established sources to ensure accuracy [20].
-
University of Sheffield:
- Sheffield has created principles to guide the use of GenAI in learning and teaching, focusing on fostering critical AI literacy among students and staff [21].
- The university has also developed a toolkit as part of the SATLE-funded (AI)²ed project, which addresses academic integrity and the use of AI in education [22].
-
University College Cork:
-
Durham University:
- Durham has introduced a micro-course exploring the use of GenAI tools in education, aiming to enhance AI literacy among students and staff [26].
3.3 Practical Applications and Case Studies
UK universities are leveraging GenAI tools in various practical applications to enhance teaching and learning:
-
Personalized Learning:
-
Innovative Assessment Methods:
- Universities are revising assessment designs to incorporate critical thinking and creativity, allowing students to use GenAI tools for specific parts of their tasks [29] [30].
- Competency-based learning, supported by GenAI, provides detailed feedback on student performance and assesses their ability to apply concepts in real-world scenarios [31].
-
AI Literacy Programs:
- Institutions are developing AI literacy programs for both students and staff to ensure they understand the strengths and limitations of GenAI tools [32] [33].
- Training sessions and resources are being provided to help academic staff integrate GenAI into their teaching practices effectively [34] [35].
-
Collaborative Projects:
- The University of Birmingham has initiated a project to capture examples of GenAI applications across disciplines and share best practices internally. This project includes creating multimedia case studies and a transferable framework for GenAI educational practices [36].
-
Addressing Academic Integrity:
- Universities are implementing measures to uphold academic integrity, such as using in-class assessments, providing clear guidelines on the use of GenAI, and fostering an ethical learning environment [24].
3.4 Challenges and Concerns
Despite the progress, UK universities face several challenges in integrating GenAI into education:
- Academic Integrity: The potential for plagiarism and misuse of GenAI tools remains a significant concern. Universities are addressing this by revising academic conduct policies and developing detection tools [37].
- Ethical and Privacy Issues: Concerns about data privacy, bias in AI-generated outputs, and the ethical implications of using GenAI in education are being actively discussed [37] [38].
- Staff Training and Support: Many academic staff feel inadequately equipped to integrate GenAI into their teaching practices, highlighting the need for ongoing training and support [39].
3.5 Synthesis
UK universities are at the forefront of integrating GenAI into higher education, adopting a proactive approach to address its challenges and harness its potential. By developing comprehensive policies, fostering AI literacy, and implementing innovative teaching and assessment methods, these institutions are preparing students and staff for an AI-driven future. However, ongoing efforts are needed to address ethical concerns, ensure equitable access, and provide adequate training and support for academic staff. As GenAI continues to evolve, UK universities must remain adaptable and collaborative to maximize its benefits while mitigating its risks.
4. Risks to Students’ Future Career Prospects
The rapid integration of Generative AI into various industries poses significant risks to students who are not adequately educated about its use. This section explores the potential challenges and disadvantages that students may face in their future career prospects if they lack proper GenAI education and training.
4.1 Inability to Compete in an AI-Driven Job Market
Generative AI is becoming a critical tool across industries, with 90% of future content expected to be AI-generated. Many industries, including healthcare, finance, marketing, and education, are increasingly relying on AI technologies, making AI literacy a fundamental skill for employability [40] [41]. Students who are not educated about generative AI risk being unprepared for roles that demand proficiency in AI tools, such as natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and data analysis.
A survey revealed that 62% of workers feel unprepared to use generative AI effectively, highlighting a significant skills gap [42]. This gap is particularly concerning as 82% of executives believe that at least half of the AI skills gap must be addressed through upskilling rather than hiring [43]. Without education in generative AI, students may struggle to secure jobs in a competitive market where AI proficiency is increasingly valued.
4.2 Missed Opportunities for High-Demand Roles
Generative AI is creating new job opportunities while simultaneously automating routine tasks. For example, roles in data analytics, STEM fields, and IT are experiencing increased demand due to AI integration [44] [45]. However, students who lack AI literacy may be excluded from these opportunities, as they are unable to meet the technical requirements of these roles.
Moreover, generative AI is expected to influence 4.5 times the number of jobs it replaces, emphasizing the need for skills that complement AI technologies [46]. Students who are not educated about generative AI may find themselves limited to roles that are more susceptible to automation, such as clerical work, which is highly exposed to technological disruption [47].
4.3 Over-Reliance on Outdated Skills
The rapid evolution of generative AI is rendering traditional skills obsolete. For instance, repetitive and routine-oriented tasks are increasingly being automated, leaving employees to focus on more complex, creative, and people-oriented tasks [48]. Students who are not trained in generative AI may continue to rely on outdated skills, making them less adaptable to the changing demands of the workforce [49].
The average half-life of job skills is approximately five years, meaning that skills acquired today may become irrelevant in the near future [50]. Without education in generative AI, students risk falling behind in a job market that prioritizes adaptability and continuous learning [41].
4.4 Increased Risk of Job Displacement
Generative AI is expected to automate up to 30% of tasks in certain industries, with lower-wage jobs being 14 times more likely to be affected [51] [52]. Students who are not educated about generative AI may find themselves disproportionately impacted by job displacement, particularly in roles that do not require advanced technical skills.
In the UK, it is estimated that AI could displace around 20% of existing jobs over the next 20 years, while creating approximately 7.2 million new jobs [53] [54]. However, the net job loss of 250,000 positions underscores the importance of equipping students with the skills needed to transition into emerging roles [55].
4.5 Lack of Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills
Generative AI tools, such as ChatGPT, can assist with tasks like writing and brainstorming, but over-reliance on these tools without proper education can hinder the development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills [56]. Students who are not taught how to critically evaluate AI-generated content may struggle to identify inaccuracies, biases, and logical flaws, which are essential skills in an AI-driven workplace [57].
A lack of critical thinking skills can also lead to poor decision-making and reduced employability, as employers increasingly value these competencies in roles that require human judgment and creativity [58].
4.6 Ethical and Privacy Concerns
Students who are not educated about the ethical implications of generative AI may inadvertently misuse these tools, leading to issues such as plagiarism, data privacy violations, and intellectual property disputes [59] [60]. For example, 78% of students have used AI tools in ways that could be considered dishonest, highlighting the need for ethical training [61].
Understanding the ethical challenges associated with generative AI, such as bias and misinformation, is crucial for responsible use [62] [63]. Without this knowledge, students may face reputational and legal risks in their professional lives [60].
4.7 Widening Digital Divide
The digital divide poses a significant risk to students who lack access to generative AI education. Students from disadvantaged backgrounds may be disproportionately affected, as they are less likely to have access to the resources and training needed to develop AI skills [64] [65]. This disparity can exacerbate existing inequalities in the job market, limiting opportunities for underrepresented groups [66].
4.8 Reduced Career Readiness
A lack of generative AI education can leave students unprepared for the evolving workforce. For instance, only 11% of students feel very prepared for work, and those who feel well-prepared are four times more likely to have a positive university experience [67] [68]. Educating students about generative AI can enhance their career readiness by equipping them with the skills needed to navigate an AI-driven job market [69].
4.9 Synthesis
The risks to students’ future career prospects if not educated about generative AI use are substantial. These risks include an inability to compete in the job market, missed opportunities for high-demand roles, over-reliance on outdated skills, increased job displacement, lack of critical thinking and problem-solving skills, ethical and privacy concerns, widening digital divides, and reduced career readiness. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from educational institutions, policymakers, and industry leaders to integrate generative AI education into curricula and provide students with the tools they need to succeed in an AI-driven world.
5. Adoption and Implementation of Generative AI in UK Industries
The United Kingdom has emerged as a leader in the adoption and implementation of Generative AI (GenAI) across various industries. This section examines the current state of GenAI adoption in UK businesses, industry-specific applications, and future projections for its use in the UK job market.
5.1 Current State of Adoption
The UK AI market is valued at over £21 billion and is expected to grow to £1 trillion by 2035 [70]. Approximately 68% of large companies, 33% of medium-sized companies, and 15% of small companies in the UK have incorporated at least one AI technology [71]. The adoption of GenAI in the UK is particularly noteworthy:
- High Adoption Rates: Only China surpasses the UK in the proportion of organizations using GenAI [72].
- Start-Up Ecosystem: The UK has the largest number of GenAI start-ups in Europe, with over 2,361 high-growth AI companies [73] [74].
- Equity Investment: The AI market has attracted £18.1 billion in equity investment as of January 2025 [75].
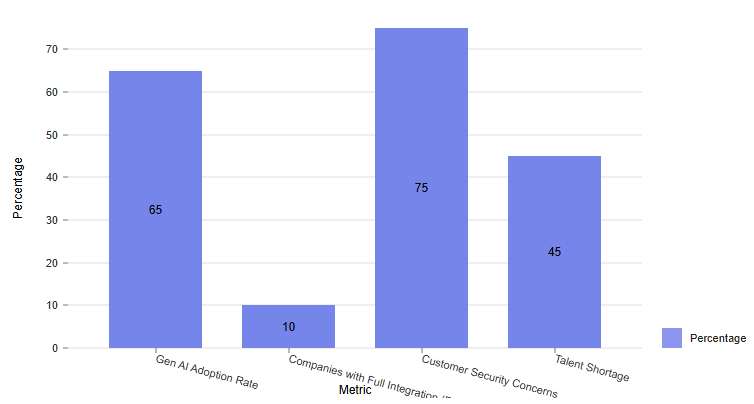
This chart illustrates the adoption rates of generative AI and the challenges faced by businesses globally, which can provide insights into trends that might be relevant to UK businesses.
5.2 Industry-Specific Applications
Generative AI is being implemented across various industries in the UK:
-
Healthcare:
-
Finance:
-
Manufacturing:
-
Retail and E-commerce:
- Retailers are using GenAI to optimize inventory management, personalize customer experiences, and enhance marketing strategies.
- In the UK, Marks & Spencer reported an 80% reduction in warehouse accidents due to AI adoption [80].
- UK retailers like H&M have launched chatbots to assist customers in finding products [81].
-
Legal Sector:
-
Energy and Utilities:
- The UK energy sector is leveraging GenAI for green energy development and environmental monitoring.
- Companies like BP and Shell are using AI to optimize processes and predict scenarios for well drilling [84].
-
Media and Entertainment:
- The media industry is using GenAI for content creation, sentiment analysis, and targeted advertising.
5.3 Public Sector Integration
The UK Government is leveraging GenAI to enhance public services:
- Efficiency Gains: AI could save the public sector up to £38 billion annually by automating tasks and improving productivity [85].
- Healthcare Innovations: AI is enabling 3.7 million additional GP appointments weekly and reducing administrative burdens [76] [86].
- Policing: AI tools are freeing up the equivalent of 160,000 police officers [87].
5.4 Future Projections for Generative AI in the UK Job Market
The adoption of GenAI in the UK is expected to have significant impacts on the job market:
-
Job Displacement and Creation:
- By 2030, up to 30% of current hours worked could be automated, with GenAI accelerating this trend [88] [89].
- It is estimated that AI could displace around 20% of existing jobs over the next 20 years, while creating approximately 7.2 million new jobs [53] [54].
- The net job loss is projected to be around 250,000 positions [55].
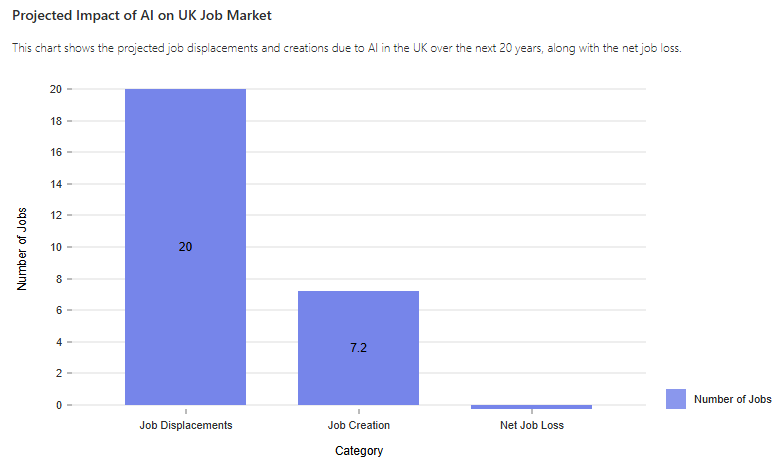 This chart shows the projected job displacements and creations due to AI in the UK over the next 20 years, along with the net job loss.
This chart shows the projected job displacements and creations due to AI in the UK over the next 20 years, along with the net job loss.
-
Sector-Specific Impacts:
-
Regional and Demographic Variations:
- London and the South East are likely to be the most affected regions, particularly in high-paying sectors like finance and insurance [94] [95].
- Women are expected to be disproportionately impacted, as they are overrepresented in roles that are highly automatable, such as office support and customer service [96].
-
Demand for AI and Digital Skills:
-
Shift Towards Hybrid Skillsets:
- The rise of GenAI will necessitate a shift towards hybrid skillsets that combine technical expertise with soft skills [99] [100].
- Critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration will become increasingly important as workers are required to complement AI capabilities rather than compete with them [99] [100].
-
Lifelong Learning and Reskilling:
-
Emerging Roles and Career Pathways:
5.5 Economic Impact
The adoption of GenAI is expected to have a significant economic impact in the UK:
- Research commissioned by Google Cloud estimates that GenAI could create over £400 billion in value across the UK economy by 2030 [105].
- GenAI has the potential to add £144 billion annually to the UK economy, equivalent to a 6.3% increase in GDP.
- GenAI could boost labor productivity by 0.1% to 0.6% annually through 2040, transforming the efficiency of various industries [106].
5.6 Challenges in Adoption
Despite the rapid adoption of GenAI, UK businesses face several challenges:
Data Privacy and Security: Concerns about data security and compliance with regulations such as the EU AI Act are significant barriers [107].
Workforce Readiness: Only 34% of public administration managers in the UK believe their workforce has the skills to leverage AI effectively [108].
Integration Issues: Businesses often struggle to integrate GenAI into existing IT infrastructures [109].
Ethical Concerns: Employers are prioritizing skills related to ethical AI, such as data bias mitigation and model explainability [110].
5.7 Synthesis
The adoption and implementation of Generative AI in UK industries are progressing rapidly, with significant impacts expected across various sectors. While GenAI offers substantial opportunities for innovation, efficiency gains, and economic growth, it also presents challenges related to job displacement, skill gaps, and ethical considerations. As the UK continues to lead in GenAI adoption, addressing these challenges through targeted policies, education, and industry collaboration will be crucial to fully realizing the potential of this transformative technology.
6. UK Policies and Initiatives for Generative AI in Education and Industry
The United Kingdom has developed a comprehensive set of policies and initiatives to support the integration of Generative AI (GenAI) in education and industry. This section explores the key strategic frameworks, educational initiatives, and industry-focused programs that are shaping the landscape of GenAI development and implementation in the UK.
6.1 Strategic Frameworks and Policies
6.1.1 AI Opportunities Action Plan
The UK Government’s AI Opportunities Action Plan, unveiled in January 2025, outlines a comprehensive strategy to leverage AI for economic growth and public service enhancement. Key elements include:
- 50 Recommendations: These focus on expanding AI infrastructure, increasing AI talent, and fostering AI adoption across sectors [111] [112].
- AI Growth Zones: Establishment of zones to accelerate AI development, including data centers and innovation hubs [113] [114].
- National Data Library: Creation of a repository featuring high-impact datasets to support AI research and development [115] [116].
- AI Skills Development: Training tens of thousands of AI professionals by 2030 through apprenticeships, higher education, and reskilling programs [117] [118].
- Public Sector AI Adoption: Encouraging large-scale AI integration in public services, such as healthcare and education [119] [120].
6.1.2 Turing AI Fellowships
The Turing AI Fellowships are a flagship initiative aimed at attracting and retaining top AI researchers. Key features include:
- £46 Million Investment: Funding to support world-leading AI research and innovation [121] [122].
- Focus on Ethics and Responsibility: Embedding ethical considerations into AI research and development [123] [124].
- Cross-Sector Collaboration: Encouraging partnerships between academia, industry, and government [125] [126].
6.1.3 Responsible AI UK Programme
The Responsible AI UK (RAI UK) programme, led by the University of Southampton and backed by UK Research and Innovation (UKRI), focuses on addressing societal challenges posed by AI. Key initiatives include:
- £10.5 Million Funding: Allocated to keystone projects in health, law enforcement, and financial services [127].
- Participatory Harm Auditing: Developing methodologies to assess the societal impact of AI [128].
- Focus on Large Language Models (LLMs): Addressing limitations and uncertainties in their use [129].
6.2 Initiatives in Education
6.2.1 Russell Group Principles on Generative AI in Education
The Russell Group of Universities has developed five guiding principles to address the use of generative AI in education:
- Supporting students and staff to become AI-literate.
- Equipping staff to guide students in using GenAI tools effectively.
- Adapting teaching and assessment to incorporate ethical AI use.
- Ensuring academic rigor and integrity.
- Promoting collaboration to share best practices [130] [131].
These principles emphasize the ethical and responsible use of GenAI while preparing students for AI-driven workplaces [132] [133].
6.2.2 Generative AI in Higher Education
Generative AI is transforming higher education in the UK through various initiatives:
- Integration into Curricula: Universities are adapting teaching and assessment methods to incorporate GenAI tools [134] [135].
- AI Literacy Programs: Efforts to ensure students and staff understand the opportunities, limitations, and ethical considerations of GenAI [136] [137].
- Micro-Courses: Institutions like Durham University have developed courses to explore the use of GenAI in learning [138].
6.2.3 Department for Education (DfE) Initiatives
The DfE is actively supporting the integration of GenAI in education:
- Reducing Administrative Burdens: Using GenAI to streamline tasks such as lesson planning and feedback [139] [140].
- Innovation Funding: Supporting the development of AI tools for education through competitions and grants [141].
- Guidance for Safe Use: Collaborating with schools and colleges to ensure the responsible adoption of GenAI [142] [143].
6.3 Initiatives in Industry
6.3.1 AI Growth Zones
The UK government has established AI Growth Zones to accelerate AI development and adoption:
- These zones provide infrastructure support, including data centers and innovation hubs [113] [114].
- They aim to create ecosystems that foster collaboration between academia, industry, and government in AI research and development.
6.3.2 National Data Library
The creation of a National Data Library is a key initiative to support AI research and development:
- This repository will feature high-impact datasets across various sectors [115] [116].
- It aims to provide researchers and businesses with access to quality data, crucial for training and improving AI models.
6.3.3 AI Skills Development Programs
The UK government has initiated several programs to address the AI skills gap:
- Apprenticeships, higher education programs, and reskilling initiatives aim to train tens of thousands of AI professionals by 2030 [117] [118].
- These programs focus on developing both technical AI skills and the ability to apply AI in various industry contexts.
6.3.4 Public Sector AI Adoption
The government is encouraging large-scale AI integration in public services:
- Initiatives in healthcare, education, and other public sectors aim to improve efficiency and service delivery [119] [120].
- For example, the NHS is exploring GenAI to address challenges such as rising healthcare costs and hospital waiting lists [76].
6.4 Studies and Reports
Several studies and reports have been commissioned to assess the impact and potential of GenAI in the UK:
6.4.1 Deloitte’s Study on GenAI in the UK
A Deloitte report highlights the transformative impact of GenAI on UK businesses:
- Increased Trust: 72% of leaders report increased trust in AI since the emergence of GenAI [144].
- Optimism About Benefits: 71% believe GenAI can improve products and services, while 70% see potential for better work experiences [145] [146].
6.4.2 Public First Research
Research commissioned by Google Cloud estimates that GenAI could create over £400 billion in value across the UK economy by 2030 [105].
6.4.3 Studies on GenAI in Education
Several studies have assessed the impact of GenAI in education:
- Student Awareness and Usage: A survey found that 61% of students were aware of GenAI, with 52% having personal experience using the tools [147] [148].
- Perceived Benefits: Over half of the respondents believed that GenAI offers academic advantages and should be integrated into learning [149].
- Challenges: Concerns include plagiarism, data privacy, and lack of institutional clarity [37] [150].
6.5 Synthesis
The UK has developed a comprehensive and forward-thinking approach to integrating GenAI into education and industry. Through strategic frameworks like the AI Opportunities Action Plan, educational initiatives led by universities and the Department for Education, and industry-focused programs, the UK is positioning itself as a global leader in GenAI development and adoption.
These policies and initiatives address key challenges such as skill development, ethical considerations, and infrastructure support. They also aim to create an ecosystem that fosters innovation, collaboration, and responsible AI use across various sectors.
However, the rapid pace of GenAI development means that these policies and initiatives will need to be continuously reviewed and updated. Ongoing collaboration between government, academia, and industry will be crucial to ensure that the UK remains at the forefront of GenAI innovation while addressing potential risks and ethical concerns.
7. Conclusion
The integration of Generative AI (GenAI) into education and industry in the United Kingdom presents both significant opportunities and challenges. This report has explored the multifaceted impacts of GenAI on academic integrity, student futures, and industry adoption, with a particular focus on the UK context.
7.1 Key Findings
GenAI in UK Higher Education: UK universities are proactively developing policies and initiatives to integrate GenAI into education while maintaining academic integrity. The Russell Group’s guiding principles and institutional initiatives demonstrate a commitment to fostering AI literacy and ethical use of GenAI tools.
Risks to Students’ Future Career Prospects: Students who lack education in GenAI face significant risks to their future career prospects. These risks include reduced competitiveness in the job market, missed opportunities for high-demand roles, over-reliance on outdated skills, and potential job displacement. The need for critical thinking, ethical awareness, and adaptability in an AI-driven workforce is paramount.
Adoption of GenAI in UK Industries: The UK is emerging as a leader in GenAI adoption across industries, with significant investments and initiatives driving innovation and economic growth. Sectors such as healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and retail are leveraging GenAI to enhance productivity, improve customer experiences, and drive innovation.
Future Projections for the UK Job Market: GenAI is expected to have a significant impact on the UK job market, with projections indicating both job displacements and creations. The need for AI-related skills and hybrid skillsets that combine technical expertise with soft skills is expected to grow substantially.
UK Policies and Initiatives: The UK government has developed comprehensive policies and initiatives to support the integration of GenAI in education and industry. These include strategic frameworks like the AI Opportunities Action Plan, educational initiatives, and industry-focused programs aimed at fostering innovation, skill development, and responsible AI use.
7.2 Implications and Recommendations
Education and Skill Development: There is an urgent need for educational institutions to integrate GenAI literacy into curricula at all levels. This includes not only technical skills but also critical thinking, ethical considerations, and the ability to work alongside AI systems.
Industry Adaptation: UK businesses across all sectors should prioritize the adoption of GenAI technologies and the development of AI-related skills within their workforce. This may involve partnerships with educational institutions and government initiatives to bridge the skills gap.
Policy and Regulation: Continued development and refinement of policies and regulations around GenAI use are essential. These should address ethical concerns, data privacy, and the potential socioeconomic impacts of widespread AI adoption.
Ethical Considerations: As GenAI becomes more prevalent, there is a need for ongoing dialogue and research into the ethical implications of its use in education and industry. This includes addressing issues of bias, transparency, and accountability in AI systems.
Inclusive Growth: Efforts should be made to ensure that the benefits of GenAI are distributed equitably across society. This includes addressing the digital divide and providing support for workers in industries most likely to be disrupted by AI.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Given the rapid pace of AI development, all stakeholders – including educators, students, industry leaders, and policymakers – must commit to continuous learning and adaptation to keep pace with technological advancements.
7.3 Future Outlook
The integration of Generative AI into education and industry in the UK is poised to bring about transformative changes. While challenges exist, particularly in terms of job market disruption and ethical considerations, the potential benefits in terms of innovation, productivity, and economic growth are substantial.
The UK’s proactive approach to GenAI adoption, as evidenced by its comprehensive policies and initiatives, positions it well to harness these benefits. However, success will depend on the ability of all stakeholders to collaborate effectively, adapt to rapid technological changes, and address the societal implications of widespread AI adoption.
As GenAI continues to evolve, ongoing research, policy development, and public dialogue will be crucial to ensure that its integration into education and industry serves the best interests of society as a whole.
References
- UK universities draw up guiding principles on generative AI | Artificial intelligence (AI). https://dailylocalnews.co.uk
- UK universities draw up guiding principles on generative AI | Artificial intelligence (AI). https://dailylocalnews.co.uk
- UK universities draw up guiding principles on generative AI | Artificial intelligence (AI). https://dailylocalnews.co.uk
- UK universities draw up guiding principles on generative AI | Artificial intelligence (AI). https://dailylocalnews.co.uk
- UK universities draw up guiding principles on generative AI | Artificial intelligence (AI). https://dailylocalnews.co.uk
- UK universities draw up guiding principles on generative AI | Artificial intelligence (AI). https://dailylocalnews.co.uk
- UK universities draw up guiding principles on generative AI | Artificial intelligence (AI). https://dailylocalnews.co.uk
- U.K.'s Leading Universities draw up 5 Guiding Principles on Generative AI. https://www.linkedin.com
- UK universities draw up guiding principles on generative AI | Artificial intelligence (AI). https://dailylocalnews.co.uk
- Leading UK universities issue joint statement on the use of AI | DailyAI. https://dailyai.com
- Generative Artificial Intelligence and its role within teaching, learning and assessment. https://www.birmingham.ac.uk
- Generative Artificial Intelligence and its role within teaching, learning and assessment. https://www.birmingham.ac.uk
- Generative Artificial Intelligence and its role within teaching, learning and assessment. https://www.birmingham.ac.uk
- Generative Artificial Intelligence and its role within teaching, learning and assessment. https://www.birmingham.ac.uk
- Use of generative AI tools to support learning | University of Oxford. https://www.ox.ac.uk
- Use of generative AI tools to support learning | University of Oxford. https://www.ox.ac.uk
- An introduction to the use of generative AI tools in teaching. https://www.ctl.ox.ac.uk
- An introduction to the use of generative AI tools in teaching. https://www.ctl.ox.ac.uk
- An introduction to the use of generative AI tools in teaching. https://www.ctl.ox.ac.uk
- Use of generative AI tools to support learning | University of Oxford. https://www.ox.ac.uk
- Navigating the Future: Higher Education policies and guidance on generative AI - Artificial intelligence. https://nationalcentreforai.jiscinvolve.org
- Navigating the Future: Higher Education policies and guidance on generative AI - Artificial intelligence. https://nationalcentreforai.jiscinvolve.org
- Frontiers Publishing Partnerships | Generative AI in Higher Education: Balancing Innovation and Integrity. https://www.frontierspartnerships.org
- Frontiers Publishing Partnerships | Generative AI in Higher Education: Balancing Innovation and Integrity. https://www.frontierspartnerships.org
- Frontiers Publishing Partnerships | Generative AI in Higher Education: Balancing Innovation and Integrity. https://www.frontierspartnerships.org
- Navigating the Future: Higher Education policies and guidance on generative AI - Artificial intelligence. https://nationalcentreforai.jiscinvolve.org
- 20 Generative AI Case Studies [2025]. https://digitaldefynd.com
- 20 Generative AI Case Studies [2025]. https://digitaldefynd.com
- Frontiers Publishing Partnerships | Generative AI in Higher Education: Balancing Innovation and Integrity. https://www.frontierspartnerships.org
- Frontiers Publishing Partnerships | Generative AI in Higher Education: Balancing Innovation and Integrity. https://www.frontierspartnerships.org
- Frontiers Publishing Partnerships | Generative AI in Higher Education: Balancing Innovation and Integrity. https://www.frontierspartnerships.org
- Frontiers Publishing Partnerships | Generative AI in Higher Education: Balancing Innovation and Integrity. https://www.frontierspartnerships.org
- U.K.'s Leading Universities draw up 5 Guiding Principles on Generative AI. https://www.linkedin.com
- Generative Artificial Intelligence and its role within teaching, learning and assessment. https://www.birmingham.ac.uk
- U.K.'s Leading Universities draw up 5 Guiding Principles on Generative AI. https://www.linkedin.com
- Developing generative AI case studies - University of Birmingham. https://research.birmingham.ac.uk
- Frontiers | Perception of generative AI use in UK higher education. https://www.frontiersin.org
- Students’ voices on generative AI: perceptions, benefits, and challenges in higher education - International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education. https://educationaltechnologyjournal.springeropen.com
- The impact of generative AI on higher education learning and teaching: A study of educators’ perspectives - ScienceDirect. https://www.sciencedirect.com
- Generative AI Landscape [year]: Complete Guide to Industry Trends & Implementation. https://magai.co
- AI Adoption Statistics 2024: All Figures & Facts to Know. https://ventionteams.com
- Generative AI Use Cases Across Industries: A Strategic 2025 Report. https://hatchworks.com
- How AI could revolutionise NHS healthcare - British Politics and Policy at LSE. https://blogs.lse.ac.uk
- Real-world gen AI use cases from the world’s leading organizations | Google Cloud Blog. https://cloud.google.com
- UK financial services drag feet on AI adoption amid uncertainty. https://www.consultancy.uk
- Top Generative AI Use Cases by Industry. https://indatalabs.com
- UK Artificial Intelligence (AI) Statistics And Trends In 2025. https://www.forbes.com
- Generative AI in Energy and Utilities Sector Use Cases & Real-Life Examples. https://masterofcode.com
- Generative AI in Energy and Utilities Sector Use Cases & Real-Life Examples. https://masterofcode.com
- Generative AI Use Cases Across Industries: A Strategic 2025 Report. https://hatchworks.com
- Top Generative AI Use Cases by Industry. https://indatalabs.com
- Generative AI Adoption in UK Reaches 83% as Environmental Concerns Mount. https://www.eweek.com
- UK Artificial Intelligence (AI) Statistics And Trends In 2025. https://www.forbes.com
- UK Artificial Intelligence (AI) Statistics And Trends In 2024 – Forbes Advisor UK. https://www.forbes.com
- LexisNexis survey finds 26% of legal professionals say they use generative AI tools at least once a month | Law Gazette. https://www.lawgazette.co.uk
- New Generative AI Study Highlights Adoption, Use and Opportunities in the Legal Industry. https://www.prnewswire.co.uk
- AI could be the key to unlocking a more efficient UK public sector. https://blog.google
- Top Generative AI Use Cases by Industry. https://indatalabs.com
- Top Generative AI Use Cases by Industry. https://indatalabs.com
- Financial Stability in Focus: Artificial intelligence in the financial system | Bank of England. https://www.bankofengland.co.uk
- AI could be the key to unlocking a more efficient UK public sector. https://blog.google
- AI could be the key to unlocking a more efficient UK public sector. https://blog.google
- AI Adoption: Statistics, Benefits, and Challenges for 2025 | Cledara. https://www.cledara.com
- UK Artificial Intelligence (AI) Statistics And Trends In 2025. https://www.forbes.com
- UK Artificial Intelligence (AI) Statistics And Trends In 2025. https://www.forbes.com
- AI Adoption Statistics 2024: All Figures & Facts to Know. https://ventionteams.com
- A new future of work: The race to deploy AI and raise skills in Europe and beyond. https://www.mckinsey.com
- Tommie Experts: Generative AI’s Real-World Impact on Job Markets - Newsroom | University of St. Thomas. https://news.stthomas.edu
- Up to 8 million UK jobs at risk from AI unless government acts, finds IPPR | IPPR. https://www.ippr.org
- Whatâs the future of generative AI? An early view in 15 charts. https://www.mckinsey.com
- The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier. https://www.mckinsey.com
- GenAI: Which industries and sectors have the greatest potential for value creation?. https://www.strategyand.pwc.com
- The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier. https://www.mckinsey.com
- Generative AI, the American worker, and the future of work. https://www.brookings.edu
- The Impact of AI on the Labour Market. https://institute.global
- How will generative AI affect students and employment?. https://luminate.prospects.ac.uk
- How will generative AI affect students and employment?. https://luminate.prospects.ac.uk
- UK Artificial Intelligence (AI) Statistics And Trends In 2024 – Forbes Advisor UK. https://www.forbes.com
- Generative AI and the future of work in America. https://www.mckinsey.com
- Finance workers in London to be the most impacted because of AI: Study. https://www.computerworld.com
- Finance workers in London to be the most impacted because of AI: Study. https://www.computerworld.com
- Generative AI and the future of work in America. https://www.mckinsey.com
- The Growing Demand for AI Skills and Expertise in the Job Market. https://www.utsa.edu
- Red Hat: AI Is the Most In-Demand Skill in the UK for 2024. https://www.techrepublic.com
- GenAI: Which industries and sectors have the greatest potential for value creation?. https://www.strategyand.pwc.com
- The next industrial revolution? Building a future UK workforce with generative AI. https://www.peoplemanagement.co.uk
- Crucial Skills Gaps in the UK Include AI and Strategic Thinking, According to Red Hat. https://www.techrepublic.com
- How Generative AI Is Changing The Future Of Work. https://www.oliverwymanforum.com
- The AI Skills Gap and How to Address It. https://www.informationweek.com
- Crucial Skills Gaps in the UK Include AI and Strategic Thinking, According to Red Hat. https://www.techrepublic.com
- AI Job Market 2025: Trends and Opportunities Across the US. https://www.dice.com
- The AI Skills Gap and How to Address It. https://www.informationweek.com
- Generative AI And The Future Of Jobs. https://www.forbes.com
- Generative AI: hopes, controversies and the future of faculty roles in education. https://www.emerald.com
- The Impact of AI on the Labour Market. https://institute.global
- The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier. https://www.mckinsey.com
- AI Literacy Essentials For Students: Preparing For The Future. https://www.innovativeeducators.org
- What is AI Literacy? A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners | DataCamp. https://www.datacamp.com
- Preparing students for the AI-enhanced workforce. https://www.insidehighered.com
- The AI Skills Gap and How to Address It. https://www.informationweek.com
- How Is AI Impacting the Job Market?. https://www.linqto.com
- How Is AI Impacting the Job Market?. https://www.linqto.com
- Generative AI and preparing for a shift to skills-based hiring. https://www.cio.com
- Generative AI and Jobs: A global analysis of potential effects on job quantity and quality.. https://www.ilo.org
- Gen AI is here to stay — here are 5 skills to help you stay relevant in the changing job market. https://www.cnbc.com
- Generative AI and preparing for a shift to skills-based hiring. https://www.cio.com
- The AI Skills Gap and How to Address It. https://www.informationweek.com
- Generative AI and the future of work in America. https://www.mckinsey.com
- Generative AI: How will it affect future jobs and workflows?. https://www.mckinsey.com
- How will generative AI affect students and employment?. https://luminate.prospects.ac.uk
- How will generative AI affect students and employment?. https://luminate.prospects.ac.uk
- How will generative AI affect students and employment?. https://luminate.prospects.ac.uk
- The Risks and Benefits of Generative AI in Education - LearnSafe. https://learnsafe.com
- AI Literacy, Explained. https://www.edweek.org
- The AI Skills Gap and How to Address It. https://www.informationweek.com
- Managing the risks of generative AI. https://www.pwc.com
- Generative AI Ethics: 11 Biggest Concerns and Risks | Informa TechTarget. https://www.techtarget.com
- Generative AI in Education: Impact, Ethics, and Use Cases. https://litslink.com
- Artificial intelligence literacy for technology education. https://www.sciencedirect.com
- LibGuides: Artificial Intelligence and Generative AI for Media & Journalism: AI Literacy Resources. https://guides.lib.unc.edu
- Benefits and risks of generative Artificial Intelligence in classrooms. https://conecta.tec.mx
- Unlocking potential: How Generative AI can help enhance career readiness. https://teachforall.org
- Tommie Experts: Generative AI’s Real-World Impact on Job Markets - Newsroom | University of St. Thomas. https://news.stthomas.edu
- Preparing students for the AI-enhanced workforce. https://www.insidehighered.com
- Preparing students for the AI-enhanced workforce. https://www.insidehighered.com
- Unlocking potential: How Generative AI can help enhance career readiness. https://teachforall.org
- UK Government launches AI Opportunities Action Plan. https://www.mishcon.com
- Unpacking the UK’s AI Action Plan | Clifford Chance. https://www.cliffordchance.com
- UK Government launches AI Opportunities Action Plan. https://www.mishcon.com
- The UK’s AI Action Plan: Bold vision, bigger challenges - University of Birmingham. https://www.birmingham.ac.uk
- UK Government launches AI Opportunities Action Plan. https://www.mishcon.com
- The UK’s AI moment: An ambitious new plan for innovation and growth. https://www.techuk.org
- AI Opportunities Action Plan - a summary. https://www.bcs.org
- The UK’s AI Action Plan: Bold vision, bigger challenges - University of Birmingham. https://www.birmingham.ac.uk
- UK Government launches AI Opportunities Action Plan. https://www.mishcon.com
- The UK’s AI moment: An ambitious new plan for innovation and growth. https://www.techuk.org
- Turing Artificial Intelligence Fellowships. https://www.gov.uk
- World-leading researchers named as Turing AI fellows. https://www.ukri.org
- Turing Artificial Intelligence Fellowships. https://www.gov.uk
- Five Turing AI fellowships named | News | Research live. https://rl-resources.cms.ama.uk.com
- Turing Artificial Intelligence Fellowships. https://www.gov.uk
- Turing AI World-Leading Researcher Fellowships. https://research-office.ed.ac.uk
- On the Russell Group principles on AI in education. https://medium.com
- Russell Group universities set out principles for AI in education. https://techmonitor.ai
- Principles on the use of generative AI tools in education. https://www.russellgroup.ac.uk
- The UK’s top universities reached an agreement on how to deal with generative AI. https://qz.com
- £12 million for UK projects to address rapid AI advances. https://www.ukri.org
- £12 million for UK projects to address rapid AI advances. https://www.ukri.org
- £12 million for UK projects to address rapid AI advances. https://www.ukri.org
- Russell Group Universities issue guidelines on how students can use ChatGPT in their studies | Regulatory Blog | Kingsley Napley. https://www.kingsleynapley.co.uk
- The UK’s top universities reached an agreement on how to deal with generative AI. https://qz.com
- On the Russell Group principles on AI in education. https://medium.com
- Principles on the use of generative AI tools in education. https://www.russellgroup.ac.uk
- Navigating the Future: Higher Education policies and guidance on generative AI - Artificial intelligence. https://nationalcentreforai.jiscinvolve.org
- Generative artificial intelligence (AI) in education. https://www.gov.uk
- Generative artificial intelligence (AI) in education. https://www.gov.uk
- Generative artificial intelligence (AI) in education. https://www.gov.uk
- Generative artificial intelligence (AI) in education. https://www.gov.uk
- Generative artificial intelligence (AI) in education. https://www.gov.uk
- Frontiers | Perception of generative AI use in UK higher education. https://www.frontiersin.org
- Frontiers | Perception of generative AI use in UK higher education. https://www.frontiersin.org
- Frontiers | Perception of generative AI use in UK higher education. https://www.frontiersin.org
- Frontiers | Perception of generative AI use in UK higher education. https://www.frontiersin.org
- The impact of Generative AI on UK businesses: a deep dive. https://www.deloitte.com
- The impact of Generative AI on UK businesses: a deep dive. https://www.deloitte.com
- The Artificial Intelligence Top 50 UK | 2025. https://www.beauhurst.com
- The Artificial Intelligence Top 50 UK | 2025. https://www.beauhurst.com
- Generative AI: What Is It, Tools, Models, Applications and Use Cases. https://www.gartner.com
- Generative AI could save UK’s public sector up to £38 billion a year and significantly reduce waiting times - Public First. https://www.publicfirst.co.uk
- Generative AI could save UK’s public sector up to £38 billion a year and significantly reduce waiting times - Public First. https://www.publicfirst.co.uk
- AI could be the key to unlocking a more efficient UK public sector. https://blog.google
- The impact of Generative AI on UK businesses: a deep dive. https://www.deloitte.com
- The impact of Generative AI on UK businesses: a deep dive. https://www.deloitte.com
- The impact of Generative AI on UK businesses: a deep dive. https://www.deloitte.com
- Generative AI could save UK’s public sector up to £38 billion a year and significantly reduce waiting times - Public First. https://www.publicfirst.co.uk